Job # 9:
Standard test method for the slump of hydraulic cement concrete:
(ASTM C-143/C-143 M-10)
Significance:
- This test method is used in lab and in field for finding out the slump (decrease in the height of concrete when we lift up the mold).
- This test is used extensively in site works all over the world. The slump test does not measure the workability of concrete directly but it co-relates the workability with some physical measurement.
- This test method is not applicable to non-plastic and non-cohesive concrete (due to larger amount of water presence).
- This test method is used to determine the slump of plastic hydraulic cement concrete.
Slump<15mm (Non-Plastic)
Slump>15mm (Plastic)
- This test method is applicable to plastic concrete having coarse aggregate upto 37.5mm in size. If the coarse aggregate is larger than the 37.5mm then this test method is not applicable.
Apparatus:
- Abrams cone
- Thickness of metal should not be less than 1.15mm
- Base diameter = 8 in (200 mm)
- Top diameter = 4 in (100 mm)
- Height = 12 in (300 mm)
- Tamping Rod
- A round, straight steel rod, with a 5⁄8 in. (16 mm) diameter.
- The length of the tamping rod shall be at least 4 in. [100 mm] greater than the depth of the mold in which rodding is being performed, but not greater than 24 in. [600 mm] in overall length
- Ruler
- Scoop
- Concrete sample
Related theory:
Workability of concrete
ACI, 1990 “That property of freshly mixed concrete or mortar which determines the ease and homogeneity with which it can be mixed, placed, consolidated and finished”
ASTM, 1993 “That property determining the effort required to manipulate a freshly mixed quantity of concrete with minimum loss of homogeneity”
Measurement of Workability:
Workability can be determined by different techniques such as,
Slump test: (Single point workability test)
Concrete is filled in a cone with proper compaction. The cone is removed and the drop in height of concrete is noted down.
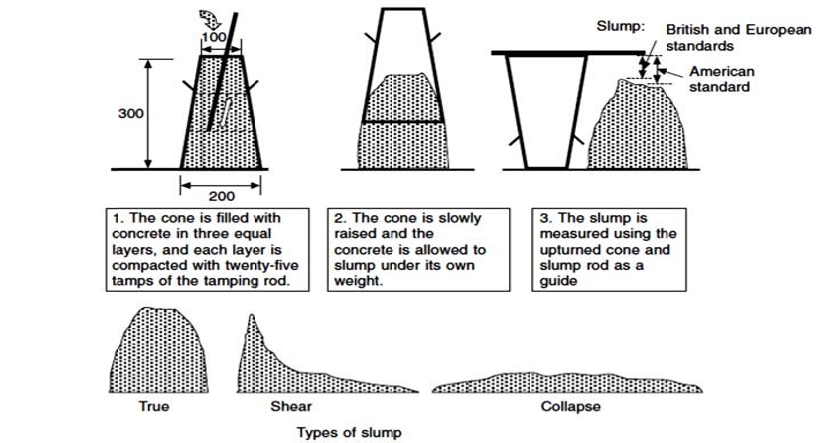
Figure from Concrete Properties by John Newman
Slump flow test: (Double point workability test)
In this test the concrete slump test is performed but instead of determining the drop in height, spread of concrete is measured.
It is used in modern techniques for high rise building and generally value greater than 500mm is specified for such test
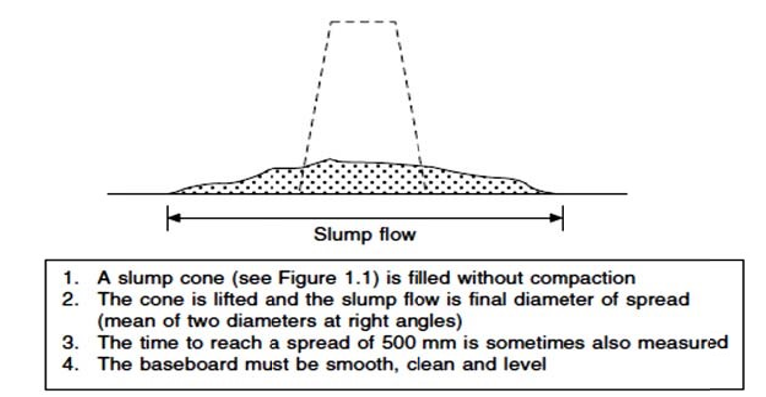
Figure from Concrete Properties by John Newman
Slump:
“The decrease in the height of concrete when the mold of standard dimensions is lifted”
Types of slump:
There are three types of slump.
- True Slump
In a true slump the concrete subsides, keeping more or less to shape
If there is bulging but consistency is maintained, then this will be true slump
- Shear Slump
In shear slump the top portion of the concrete shears off and slips sideways.
Shear slump occurs due to the lack of cohesion in mix.
- Collapse slump
In a collapse slump the concrete collapses completely
We discard the collapse slump due to the very high value of slump
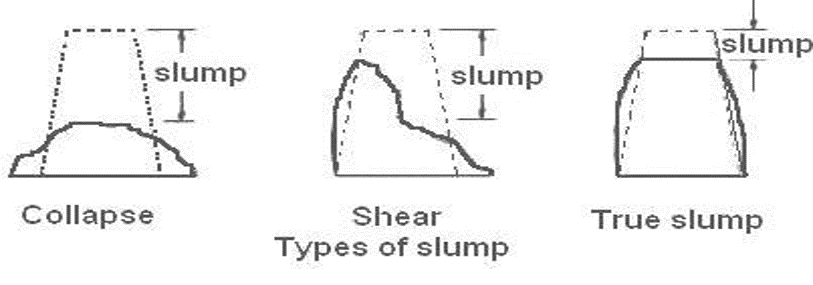
Figure showing different types of slump
Relation between workability and slump
Workability Slump (mm)
Very Low 0-25
Low 25-50
Medium 50-100
High 100-175
Note: More is the slump value more will be the workability.
Procedure:
- The mold is placed on a flat moist non-absorb surface with the smaller opening at the top. It is then held firmly in place during filling of concrete by the operator standing on two foot pieces.
- The mold is filled to a depth of 70mm and 2/3 of volume fills to a depth of 160mm.
- Each layer is given 25 strokes with the help of temping rod uniformly distributed over the cross-section of each layer.
- Rod the 2nd and 3rd layer throughout its depth so that strokes just penetrate into the under lying layer. After the top layer is rodded strike off the surface of the concrete by means of rolling motion of temping rod.
- Complete the entire test with an elapsed time of 2.5minutes. After filling, the cone is slowly lifted and the unsupported concrete slumps. The decrease in the height of concrete is called slump.
- It is measured with the nearest 5mm. at the beginning of every test, before lifting the mold the area immediately around the base of the cone should be cleaned off of concrete which may be dropped accidentally.
Observations and Calculations
Mixed ratio used (Cement:Sand:Aggregate)= 1 : 1.5: 3
Cement brand = Lucky cement
Slump Value = 2.5 inch = 63.5 mm
Comments:
- As the slump value is 63.5 mm, hence the workability of concrete is medium
- For columns, the slump value should be more
- For slabs, the slump value should be less
