Job 3
To perform direct shear test on a plane steel bar and punching shear test on steel plate
Objective:
To determine the shear strength of steel samples
Apparatus:
- 10 ton Buckton UTM
- Shear jigs
- Vernier calipers
- Steel bar
- Steel plate
Related theory:
- Shear force (V) :
A force which tends to slide one part of a section against the adjacent is known as shear force.
- Shear stress / tangential stress (
):
It is the intensity of the internal forces on a plane area when the forces are acting parallel to the section.
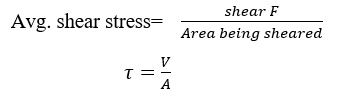
Note: A uniform shearing stress will exist when the resultant shear force passes through the centroid of the cross section being sheared.
- Types of shear stress:
- Direct shear:
If the force applied is parallel to the area being sheared, then it is direct shear.
Following are the types of direct shear.
- Single shear:
Shear stress induced due to a force causing single area of cross section to be sheared is called single shear.
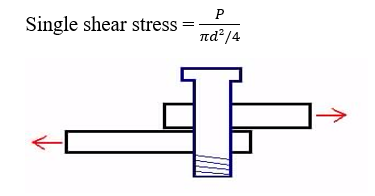
- Double shear:
Shear stress induced due to a force causing double area of cross section to be sheared.
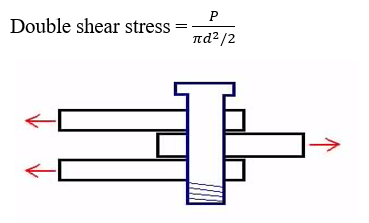
- Punching shear:
Shear stress induced due to a force causing one part to be punched into the other.
Area being sheared is again parallel to applied load.
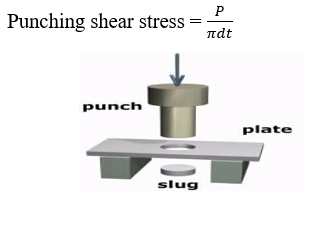
- Induced shear:
Shearing stress induced due to a force which acts at an angle to the area being sheared.
Procedure:
- Insert the specimen in position and grip one end of the attachment in the upper portion and one end in the lower position
- Switch on the UTM
- Bring the drag indicator in contact with the main indicator.
- Select the suitable range of loads and space the corresponding weight in the pendulum and balance it if necessary with the help of small balancing weights
- Operate (push) the button for driving the motor to drive the pump.
- Gradually move the head control ever in left hand direction till the specimen shears.
- Note down the load at which the specimen shears.
- Stop the machine and remove the specimen.
Repeat the experiment with other specimens.
Observations and calculations
For direct shear test on plane steel bar:
| Shear load | Diameter (d) | Avg. (d) | Area=
|
Shear strength=
|
||||
| (mm) | ||||||||
| Tons | N | D1 | D2 | D3 | mm | mm2 | MPa | Psi |
| 1.132 | 10074.8 | 6.50 | 6.55 | 6.70 | 6.58 | 34 | 296.3 | 42975 |
For punching shear test on a steel plate:
| Shear load | Diameter of jigs (d) | Avg. (d) | Plate thickness
(t) |
Shear area
) |
Shear strength=
|
|||
| (mm) | ||||||||
| Tons | N | Upper jig | Lower jig | mm | mm | mm2 | MPa | Psi |
| 2.586 | 23015.4 | 14.90 | 15.20 | 15.05 | 2.10 | 99.29 | 231.79 | 33618.9 |
