Job # 4
To carry out compression test on wooden cubes when load is applied
- Parallel to grains
- Perpendicular to the grains.
Objective:
- To determine compressive strength of wood
- To determine modulus of elasticity € and modulus of stiffness (K)
- To observe an-isotropic behavior of wood.
Apparatus:
- Wooden samples
- Vernier calipers
- Deflection gauge
- Shimadzu 500kN UTM
Related theory:
- Compressive strength:
The maximum stress that a material can bear is called its compressive strength.
- Strength:
The maximum value of stress that a material can bear.
- Modulus of elasticity:
It is the ratio of stress to strain and is determined by the slope of stress strain diagram from 0 to proportional limit. (i.e within elastic limit)

- Elasticity:
Ability of a body to retain its shape is called its elasticity.
- Stiffness (k):
It is the force required to produce unit deformation.
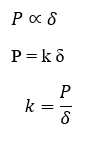
- Isotropic materials:
The materials which exhibit same properties in different directions are called isotropic. e.g. steel
- Anisotropic materials:
The materials which exhibit different properties in different directions are called an-isotropic. e.g. wood
Failure to wooden cubes when load is applied:
- Parallel to grains:
The wooden sample will take more load to fail on applying load. This is because each fiber act as a column to parallel load.
2. Perpendicular to grains:
When load is applied wooden sample will take comparatively less load because each fiber acts as beam and the failure of a single fiber will cause the failure of whole sample.
Procedure:
- Measure the cross-section and length of the specimen and record the dimensions on the data sheet. The ends of the specimens should be plane and at right angles to the axis of the specimen.
- Place the specimen in the machine.
- Apply the load continuously until the specimen fails. Record the maximum load.
- Draw a sketch, in perspective, indicating the grain of the wood and the manner of failure.
- For the specimen with the grains oriented at 90o, plot the load vs. deformation and determine the proportional limit from the curve.
- Compute the compressive strength (for the specimen with 0o grain orientation) or the proportional limit (for the specimen with 90o grain orientation).
Observations and calculations
| Specimen | L | W | H | A = L x W |
| (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm2) | |
| Parallel to grains | 52.35 | 51.8 | 48.3 | 2711.73 |
| Perpendicular to grains | 47.95 | 48.80 | 50.05 | 2339.96 |
Parallel to grains:
| Obs. | Load ‘P’ | Deflection gauge reading | Deformation ‘δ’ | %age strain=
|
σ =
|
K=
|
| (kN) | (mm) | N/mm2 | N/mm | |||
| 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||
| 2 | 5 | 106 | 0.1524 | 0.3155 | 1.843 | 32808 |
| 3 | 10 | 108 | 0.2032 | 0.4207 | 3.687 | 49212 |
| 4 | 15 | 110 | 0.254 | 0.5258 | 5.531 | 59055 |
| 5 | 20 | 113 | 0.3302 | 0.6836 | 7.375 | 60569 |
| 6 | 25 | 114 | 0.3556 | 0.7362 | 9.219 | 70303 |
| 7 | 30 | 115 | 0.381 | 0.7888 | 11.063 | 78740 |
| 8 | 35 | 117 | 0.4318 | 0.8939 | 12.906 | 81056 |
| 9 | 40 | 119 | 0.4826 | 0.9991 | 14.75 | 82901 |
| 10 | 45 | 121 | 0.5334 | 1.1043 | 16.594 | 84364 |
| 11 | 50 | 123 | 0.5842 | 1.2095 | 18.438 | 85587 |
| 12 | 55 | 124 | 0.6096 | 1.2621 | 20.282 | 90223 |
| 13 | 60 | 126 | 0.6604 | 1.3672 | 22.126 | 90854 |
| 14 | 65 | 128 | 0.7112 | 1.4724 | 23.969 | 91394 |
| 15 | 70 | 130 | 0.762 | 1.5776 | 25.813 | 91863 |
| 16 | 75 | 132 | 0.8128 | 1.6828 | 27.657 | 92273 |
| 17 | 80 | 135 | 0.889 | 1.8405 | 29.501 | 89988 |
| 18 | 85 | 138 | 0.9652 | 1.9983 | 31.345 | 88064 |
| 19 | 90 | 143 | 1.0922 | 2.2612 | 33.189 | 82402 |
| 20 | 95 | 150 | 1.27 | 2.6293 | 35.032 | 74803 |
| 21 | 99.5 | 176 | 1.9304 | 3.9966 | 36.692 | 51543 |

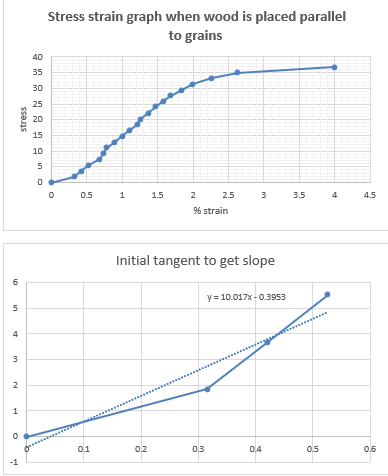
Stress strain graph when wood is placed parallel to grains
Hence slope = 10.017
Perpendicular to grains:
| Obs. | Load ‘P’ | Deflection gauge reading | Deformation ‘δ’ | %age strain=
|
σ =
|
K=
|
| (kN) | (mm) | N/mm2 | N/mm | |||
| 1 | 0 | 100 | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 103 | 0.0762 | 0.1522 | 0.4273 | 13123 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 112 | 0.3048 | 0.6089 | 0.6410 | 4921 |
| 4 | 2 | 135 | 0.889 | 1.7762 | 0.8547 | 2249 |
| 5 | 2.5 | 203 | 2.6162 | 5.2271 | 1.0683 | 955 |
| 6 | 3 | 294 | 4.9276 | 9.8453 | 1.2820 | 608 |
| 7 | 3.5 | 390 | 7.366 | 14.7172 | 1.4957 | 475 |
| 8 | 4 | 464 | 9.2456 | 18.4727 | 1.7094 | 432 |
| 9 | 4.5 | 536 | 11.0744 | 22.1266 | 1.9231 | 406 |
| 10 | 5 | 597 | 12.6238 | 25.2223 | 2.1367 | 396 |
| 11 | 5.5 | 664 | 14.3256 | 28.6225 | 2.3504 | 383 |
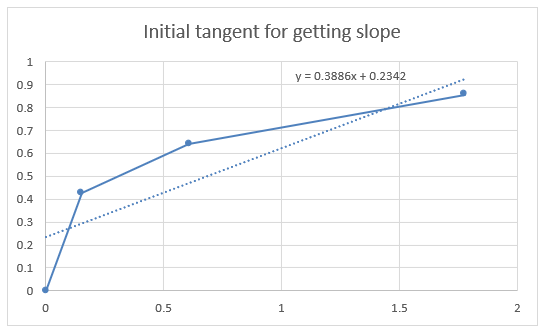
Stress to strain graph when wood is placed perpendicular to grains
Hence slope = 0.3886
