Determination of the compressive strength of mortar cubes (ASTM C-109)
Significance:
- This test method covers determination of the compressive strength of ordinary Portland cement mortars, using 2-in. or [50-mm] cube specimens.
Apparatus:
- Weighing balance
- Glass graduate
- Six 50 mm (2 in.) cube molds (ASTM)
- Hard rubber tampers 13 × 25 mm (1/2 × 1 in.) cross section and 12 to 15 cm (5 to 6 in.) in height
- Small steel trowels
- 500 grams of Ordinary Portland Cement
- 1375 grams of Ottawa Equivalent Sand
- 242 cc of water
- Testing machine
Related theory:
Compressive strength:
The resistance of material to break under compressive force is known is compressive strength.
Mortar:
The mixture of cement, fine aggregate and water is known as mortar.
It is generally used in brickwork as binding material and plastering.
Ottava sand:
Ottava is the capital city of Canada. The sand present there is granular in nature and is marked as standard sand. We will make sample of sand which will be equivalent to Ottava sand.
Procedure:
Preparation of Mortar:
- Weigh (200) gm of cement and 600g of sand.
- Take 80 ml of water in graduated glass cylinder.
- Place the dry paddle and the dry bowl in the mixing position in the mixer. Then introduce the materials for a batch into the bowl and mix in the following manner:
- Place all the mixing water in the bowl.
- Add the cement to the water, then start the mixer and mix at the low speed (140 ± 5 r/ min) for (30 s).
- Add the entire quantity of sand slowly over a (30 s) period, while mixing at slow speed.
- Stop the mixer, change to medium speed (285 +10 r/min) and mix for 30 s.
- Stop the mixer and let the mortar stand for 1.5 min. During the first (15 s) of this interval, quickly scrape down into the batch any mortar that may have collected on the side of the bowl.
- Finish by mixing for (1min) at medium speed.
Molding of Test Specimens:
- Thinly cover the interior faces of the specimen molds with oil.
- Start molding the specimens within a total time of not more than 2.5 min after completion of mixing.
- Place a layer of mortar about 25 mm (half the depth of the mold) in all the cube specimens.
- Tamp the mortar in each cube 32 times (4×8), about 4 rounds, each round to be at right angles to the other.
- The tamping pressure shall be just sufficient to insure uniform filling of the molds.
- The 4 rounds of taming shall be completed in one cube before going to the next.
- When the tamping of the first layer in all cubes is completed, fill the molds with the remaining mortar and tamp as specified for the first layer.
- Cut off the mortar to a plane surface with a straight edge.
- Keep the molds in a moist room for 20-24 hours then open them and keep the specimens in a water basin for a week.
Testing of Specimens:
- After 7 days, take the specimens out of the basin, dry them with a clean cloth, put them one after the other in the testing machine.
- The cubes must be put on one side, using extra steel plates up and down the specimen.
- Start loading in a speed of 1.4 kN /sec or (350 kg /cm2 ) in a minute
- When failure, record load and the compressive strength.
Observations & Calculations
Type of cement: Ordinary Portland cement
Manufacturer of cement: Lucky cement
| Description | ASTM specification | Specifications that we used |
| No. of molds | 6 | 4 |
| Molds size | 2″×2″ | 2.78″×2.78″ |
| C/S ratio | 1 : 2.75 | 1 : 3 |
| W/C ratio | 0.484 | 0.4 |
| Mass of cement | 500 g | 200 g |
| Mass of Ottava equivalent sand | 1375 g | 600 g |
| Volume of water | 242 ml | 80 ml |
| Cube # | Age of sample | Cube dimensions | Cube area | Maximum applied load | Compressive strength | Avg. Compressive strength | |
| days | L*W*H | mm2 | ton | N | MPa | MPa | |
| 1 | 3 | 2.78″×2.78″×2.78″ | 4986.055 | 8.75 | 87220 | 17.49 | 15.74 |
| 2 | 3 | 2.78″×2.78″×2.78″ | 4986.055 | 7 | 69776 | 13.99 | |
| 3 | 7 | 2.78″×2.78″×2.78″ | 4986.055 | 12.25 | 122108 | 24.49 | 23.99 |
| 4 | 7 | 2.78″×2.78″×2.78″ | 4986.055 | 11.75 | 117124 | 23.49 | |
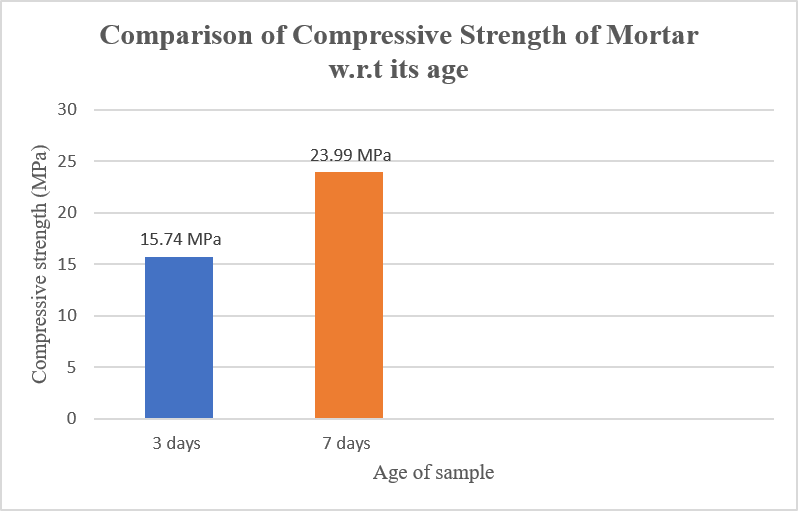
Avg. Compressive strength = 15.74 MPa for 3 days compressive strength
= 23.99 MPa for 7 days compressive strength
Comments:
- The compressive strength obtained from age 7 days mortar is greater than age 3 days mortar, which means that the mortar is still gaining its strength and it continues gaining its strength till 28 days.
- The mortar cubes were cured after the preparation and special care is taken while curing period to avoid cracking during hydration process.
- The compressive strength of 28 days ordinary Portland cement cube may go upto 10,000 psi.
